UOMOP
확률적 경사 하강법 using algorithm (boston) 본문
Stochastic Gradient Descent(확률적 경사 하강법)은 학습 데이터 셋에서 하나의 샘플만을 이용해서 가중치와 절편을 update하게 된다.
하나의 샘플만을 이용해서 선형식을 업데이트하지만 Batch Gradient Descent와 비교해보았을 때 크게 차이나지 않는 것이 특징이다.
1. 데이터 불러오기
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
boston = load_boston()
boston_df = pd.DataFrame(boston.data, columns = boston["feature_names"])
boston_df["PRICE"] = boston.target2. SGD 함수 선언
def sgd(feature, target, learning_rate, iter_epochs, verbose):
bias = np.random.rand(1,)
w1 = np.random.rand(1,)
w2 = np.random.rand(1,)
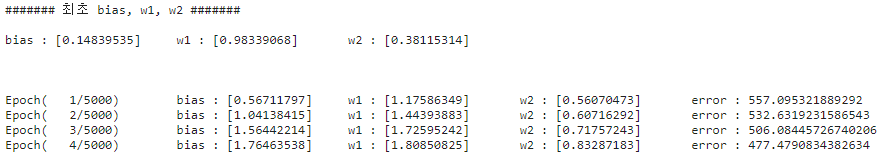
print("####### 최초 bias, w1, w2 #######\n")
print("bias : {}\tw1 : {}\tw2 : {}\n\n\n".format(bias, w1, w2))
for i in range(iter_epochs) :
sgd_index = np.random.choice(len(target), 1)
feature_1 = feature[sgd_index, 0]
feature_2 = feature[sgd_index, 1]
target_in = target[sgd_index]
N = len(target_in)
predict = bias + w1 * feature_1 + w2 * feature_2
diff = target_in - predict
bias_update = -(2/N) * learning_rate * (np.dot(np.ones((N,)), diff))
w1_update = -(2/N) * learning_rate * (np.dot(feature_1.T, diff))
w2_update = -(2/N) * learning_rate * (np.dot(feature_2.T, diff))
##########################################################################
predict_for_loss = bias + w1 * feature[:, 0] + w2 * feature[:, 1]
diff_for_loss = target - predict_for_loss
err = np.mean(np.square(diff_for_loss))
#########################################################################
bias = bias - bias_update
w1 = w1 - w1_update
w2 = w2 - w2_update
if verbose == True :
print("Epoch( {}/{})\tbias : {}\tw1 : {}\tw2 : {}\terror : {}"
.format(i+1, iter_epochs, bias, w1, w2, err))
return bias, w1, w2확률적 경사 하강법은 506개의 샘플 중에서 하나의 샘플만을 이용해서 선형식의 가중치와 절편을 업데이트하게 된다.
np.random.choice(A, B) 는 0~(A-1) 정수에서 B개 만큼 난수를 뽑아낸다.
np.random.choice을 이용해서 랜덤한 인덱스를 받고 동일한 샘플의 feature, target을 찾아서 선형식을 업데이트한다.
여기서, 주의 할 점은 loss(MSE)이다. bias, w1, w2는 한 샘플의 data만을 이용해서 update시켰지만 MSE는 모든 데이터에 값을 확인해야한다. 따로 loss을 위한 변수들을 설정해주고 MSE를 출력하였다.
3. feature 전처리 (Scaling)
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
mms = MinMaxScaler()
scaled_feature = mms.fit_transform(boston_df[["RM", "LSTAT"]])4. SGD를 통해서 가중치, 절편 확인
bias, w1, w2 = sgd(scaled_feature, boston_df["PRICE"], learning_rate = 0.01,
iter_epochs = 5000, verbose = True)5. 도출해낸 가중치, 절편으로 선형식을 완성하고, 예측 진행
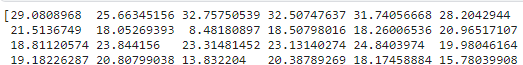
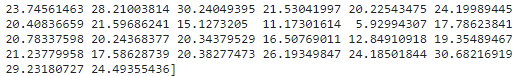
z = bias + w1 * scaled_feature[:, 0] + w2 * scaled_feature[:, 1]
print(z)6. 예측 결과를 DataFrame에 추가
boston_df["PREDICT_using_hand"] = z
boston_df.head()

'Ai > DL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Functional API (0) | 2022.02.06 |
|---|---|
| 미니배치 경사 하강법 using algorithm (boston) (0) | 2022.02.01 |
| 배치 경사 하강법 using keras (boston) (0) | 2022.02.01 |
| 배치 경사 하강법 using algorithm (boston) (0) | 2022.02.01 |
| 기본적인 케라스(keras)모델 구현 (0) | 2022.01.30 |
Comments