목록Summary (18)
UOMOP
 판다스(Pandas) - 2 : 데이터 selection 및 filtering
판다스(Pandas) - 2 : 데이터 selection 및 filtering
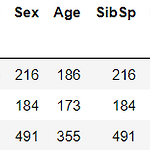
DataFrame의 []연산자 넘파이에서 []연산자는 행의 위, 열의 위치, 슬라이싱 범위 등을 지정해 데이터를 가져올 수 있다. 하지만 DataFrame 바로 뒤에 있는 '[]'안에 들어갈 수 있는 것은 컬럼 명 문자, 또는 인덱스로 변환 가능한 표현식이다. import pandas as pd titanic_df = pd.read_csv("titanic_train.csv") print("단일 컬럼 데이터 추출 : \n{}".format(titanic_df["Pclass"].head(3))) print("") print("여러 컬럼들의 데이터 추출 : \n{}".format(titanic_df[["Survived", "Pclass"]].head(3))) print("") print("[] 안에 숫자 in..
 판다스(Pandas) - 1
판다스(Pandas) - 1
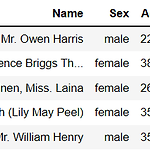
read_csv() : read_csv()를 이용하여 csv파일을 편리하게 DataFrame으로 로딩한다. read_csv()의 sep 인자를 콤마(,)가 아닌 다른 분리자로 변경하여 다른 유형의 파일로 로드 가능 import pandas as pd titanic_df = pd.read_csv("titanic_train.csv") print("titanic 변수 type : {}".format(type(titanic_df))) titanic 변수 type : head() DataFrame의 맨 앞 일부 데이터만 추출한다. default값은 5 가장 왼쪽에 있는 column이 index여서 column명이 없다. titanic_df.head() titanic_df.head(3) DataFrame의 생성 d..
ndarray 생성 - np.array() import numpy as np list1 = [1, 2, 3] print("list1 : {}".format(list1)) print("list1 type : {}".format(type(list1))) array1 = np.array(list1) print("array1 : {}".format(array1)) print("array1 type : {}".format(type(array1))) list1 : [1, 2, 3] list1 type : array1 : [1 2 3] array1 type : ndarray의 형태(shape)와 차원(dimension) import numpy as np list1 = [1, 2, 3] list2 = [2, 3, 4]..
List, Tuple, Dict에 대한 Python Built-in 확장 자료 구조 아래의 모듈이 존재 from collections import deque from collections import Counter from collections import defaultdict from collections import namedtuple 1. deque from collections import deque d = deque([2, 3, 4, 5]) print(d) d.append(6) print(d) d.appendleft(1) print(d) d.pop() print(d) deque([2, 3, 4, 5]) deque([2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) deq..
1. List(리스트) a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] a.append(10) a.append(20) print(a) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 20] a.pop() print(a) a.pop(0) print(a) a.pop(2) print(a) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10] [2, 3, 4, 5, 10] [2, 3, 5, 10] a.insert(0, 1) print(a) a.insert(3, 4) print(a) # 앞에는 자릿수, 뒤에는 설정숫자 [1, 2, 3, 5, 10] [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10] 2. tuple(튜플) 값의 변경이 불가능한 리스트 선언시 "()"를 사용 리스트의 연산, 인덱싱, 슬라이싱 등을 동일하게 사용 t = (1, 2, 3) print(t[1])..

